MOSFET Depletion Region Width Xd
Gauss’s Law
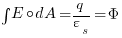 This is the electric field flux
This is the electric field flux
With a uniform charge density that is much more wide and long than it is thick you can use the following:
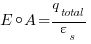
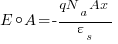
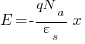 So as you progress upwards from 0 the flux increases.
So as you progress upwards from 0 the flux increases.
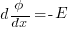
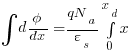
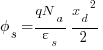
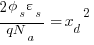
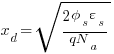
Gathering up terms and using Gauss’s law:
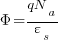

Now that we have the estimate for the depletion width Xd:
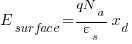
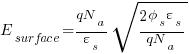
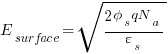
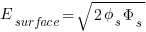
Now the total charge is
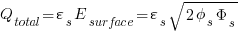
Summary
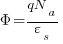 Planar Flux Density
Planar Flux Density 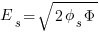
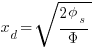
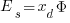
See equation: A2.1.13: CMOS Analog Design Using All Region MOSFET Modeling
Research Links
Gauss’s Law
Introduction to Solid State Devices: Chapter 10 See page 6, Body Effect coefficient page 49
0 Comments