Gates.

Quantum logic
In a famous paper of 1936, the first work ever to introduce quantum logics,[28] von Neumann first proved that quantum mechanics requires a propositional calculus substantially different from all classical logics and rigorously isolated a new algebraic structure for quantum logics. The concept of creating a propositional calculus for quantum logic was first outlined in a short section in von Neumann's 1932 work. But in 1936, the need for the new propositional calculus was demonstrated through several proofs. For example, photons cannot pass through two successive filters which are polarized perpendicularly (e.g., one horizontally and the other vertically), and therefore, a fortiori, it cannot pass if a third filter polarized diagonally is added to the other two, either before or after them in the succession. But if the third filter is added in between the other two, the photons will indeed pass through. And this experimental fact is translatable into logic as the non-commutativity of conjunction  . It was also demonstrated that the laws of distribution of classical logic,
. It was also demonstrated that the laws of distribution of classical logic, 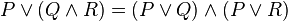 and
and  , are not valid for quantum theory. The reason for this is that a quantum disjunction, unlike the case for classical disjunction, can be true even when both of the disjuncts are false and this is, in turn, attributable to the fact that it is frequently the case, in quantum mechanics, that a pair of alternatives are semantically determinate, while each of its members are necessarily indeterminate. This latter property can be illustrated by a simple example. Suppose we are dealing with particles (such as electrons) of semi-integral spin (angular momentum) for which there are only two possible values: positive or negative. Then, a principle of indetermination establishes that the spin, relative to two different directions (e.g., x and y) results in a pair of incompatible quantities. Suppose that the state ɸ of a certain electron verifies the proposition "the spin of the electron in the x direction is positive." By the principle of indeterminacy, the value of the spin in the direction y will be completely indeterminate for ɸ. Hence, ɸ can verify neither the proposition "the spin in the direction of y is positive" nor the proposition "the spin in the direction of y is negative." Nevertheless, the disjunction of the propositions "the spin in the direction of y is positive or the spin in the direction of y is negative" must be true for ɸ. In the case of distribution, it is therefore possible to have a situation in which
, are not valid for quantum theory. The reason for this is that a quantum disjunction, unlike the case for classical disjunction, can be true even when both of the disjuncts are false and this is, in turn, attributable to the fact that it is frequently the case, in quantum mechanics, that a pair of alternatives are semantically determinate, while each of its members are necessarily indeterminate. This latter property can be illustrated by a simple example. Suppose we are dealing with particles (such as electrons) of semi-integral spin (angular momentum) for which there are only two possible values: positive or negative. Then, a principle of indetermination establishes that the spin, relative to two different directions (e.g., x and y) results in a pair of incompatible quantities. Suppose that the state ɸ of a certain electron verifies the proposition "the spin of the electron in the x direction is positive." By the principle of indeterminacy, the value of the spin in the direction y will be completely indeterminate for ɸ. Hence, ɸ can verify neither the proposition "the spin in the direction of y is positive" nor the proposition "the spin in the direction of y is negative." Nevertheless, the disjunction of the propositions "the spin in the direction of y is positive or the spin in the direction of y is negative" must be true for ɸ. In the case of distribution, it is therefore possible to have a situation in which  , while
, while  .
.
Von Neumann proposes to replace classical logics, with a logic constructed in orthomodular lattices, (isomorphic to the lattice of subspaces of the Hilbert space of a given physical system).[29]
Research Links



 . It was also demonstrated that the laws of distribution of classical logic,
. It was also demonstrated that the laws of distribution of classical logic, 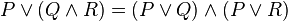 and
and  , are not valid for quantum theory. The reason for this is that a quantum disjunction, unlike the case for classical disjunction, can be true even when both of the disjuncts are false and this is, in turn, attributable to the fact that it is frequently the case, in quantum mechanics, that a pair of alternatives are semantically determinate, while each of its members are necessarily indeterminate. This latter property can be illustrated by a simple example. Suppose we are dealing with particles (such as electrons) of semi-integral spin (angular momentum) for which there are only two possible values: positive or negative. Then, a principle of indetermination establishes that the spin, relative to two different directions (e.g., x and y) results in a pair of incompatible quantities. Suppose that the state ɸ of a certain electron verifies the proposition "the spin of the electron in the x direction is positive." By the principle of indeterminacy, the value of the spin in the direction y will be completely indeterminate for ɸ. Hence, ɸ can verify neither the proposition "the spin in the direction of y is positive" nor the proposition "the spin in the direction of y is negative." Nevertheless, the disjunction of the propositions "the spin in the direction of y is positive or the spin in the direction of y is negative" must be true for ɸ. In the case of distribution, it is therefore possible to have a situation in which
, are not valid for quantum theory. The reason for this is that a quantum disjunction, unlike the case for classical disjunction, can be true even when both of the disjuncts are false and this is, in turn, attributable to the fact that it is frequently the case, in quantum mechanics, that a pair of alternatives are semantically determinate, while each of its members are necessarily indeterminate. This latter property can be illustrated by a simple example. Suppose we are dealing with particles (such as electrons) of semi-integral spin (angular momentum) for which there are only two possible values: positive or negative. Then, a principle of indetermination establishes that the spin, relative to two different directions (e.g., x and y) results in a pair of incompatible quantities. Suppose that the state ɸ of a certain electron verifies the proposition "the spin of the electron in the x direction is positive." By the principle of indeterminacy, the value of the spin in the direction y will be completely indeterminate for ɸ. Hence, ɸ can verify neither the proposition "the spin in the direction of y is positive" nor the proposition "the spin in the direction of y is negative." Nevertheless, the disjunction of the propositions "the spin in the direction of y is positive or the spin in the direction of y is negative" must be true for ɸ. In the case of distribution, it is therefore possible to have a situation in which  , while
, while  .
.